“Self-restraint is life,” forms the philosophical ideal behind the Anuvrat Movement.
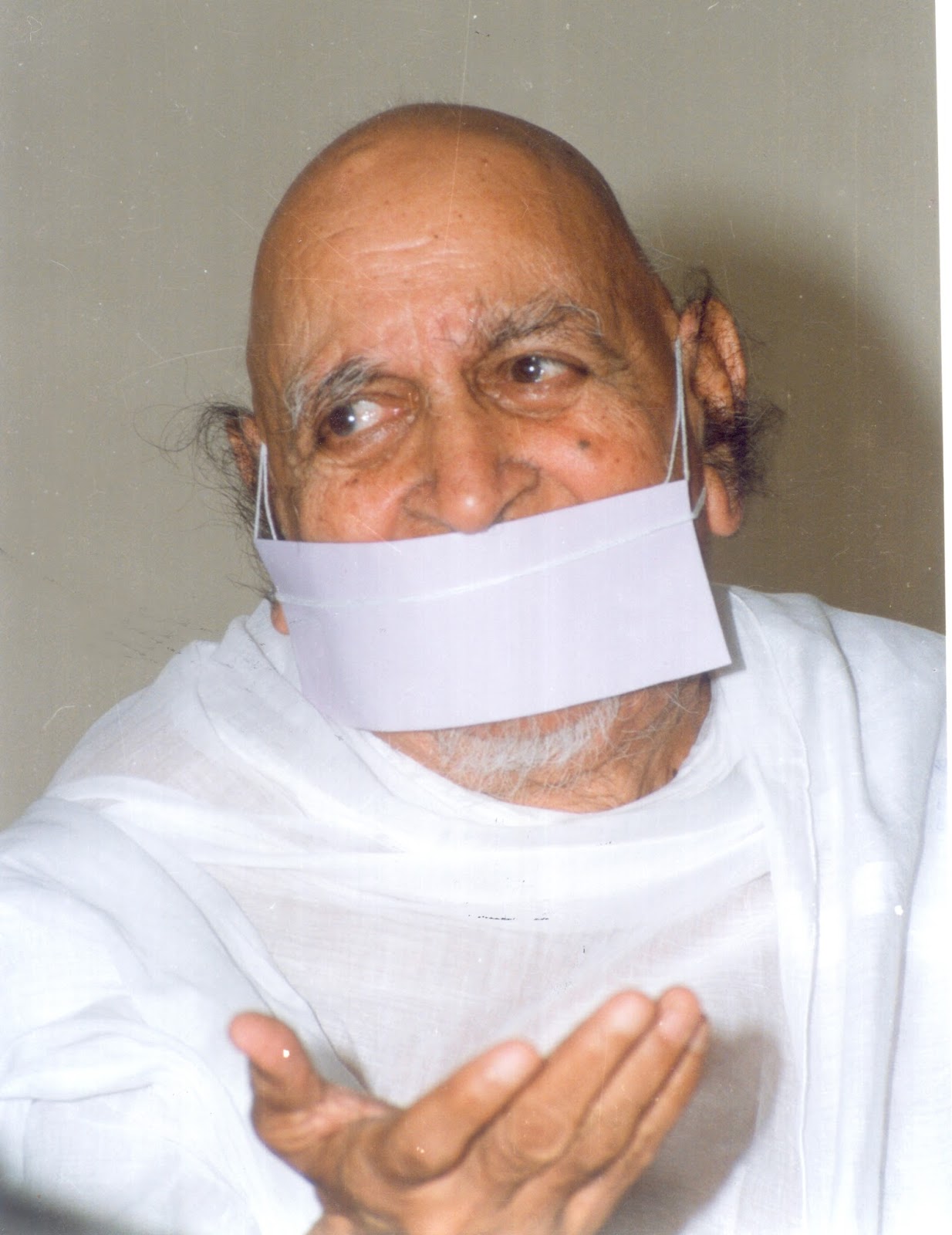
Acharya Tulsi, a celebrated monk within the Jain tradition was the founder of the Anuvrat Movement. Accepting monkhood at the age of 11, he was accredited to be the Acharya (His Holiness) of the Jain Svetambara Terapanth (Terapant
Acharya Tulsi perceived that modernization contributed to the deterioration of the moral character and value system in the pluralist Indian society. He also observed that there were aspects of his Jain tradition that could be useful in addressing such issues but they needed to be shared outside the Jain community. Therefore, at the age of 34, he conceptualized and instituted the Anuvrat Movement in October 1948. The thrust of the movement was to regenerate the character of Indians through individual self-transformation, which would eventually influence the building of a healthy society and the development of methods for fostering social justice, peace and sustainability. According to Acharya Tulsi, one cannot solve the problems of violence, human rights, poverty and the environment all at once. Instead, Acharya Tulsi thought that by employing the concept of small vows for individuals, adopted from the Jain tradition, he can develop the framework for social improvement achieved through personal actions. The Jain doctrines of Ahimsa (non-violence), Aparigraha (
Both non-violence and non-possession are pan-Indic concepts, however Anekant is unique to Jain philosophy. Anekant is the theory that truth and reality are perceived differently from diverse points of view, and that no single point of view is the complete truth. Inspired by his own study and experiences, Acharya Tulsi expanded on Anekant using it as a core concept to transcend religions and incorporate concepts of morality into a secular movement. The movement was initiated in the mid twentieth century, during the time when theories of secularization were being expanded. Acharya Tulsi’s approach recognized that the power of religious institutions was diminishing in response to secularization but spirituality was not. He wished therefore to incorporate spirituality into a secular movement without direct reference to any specific religious institution.
This work is brought to you for free and open access by the University Graduate School at FIU Digital Commons.
People Also Ask….
Who are some famous Jain businessmen in India?
- Gautam Adani of Adani Group
- Dilip Sanghvi of Sun Pharmaceuticals
- Mangal Prabhat Lodha, Real Estate
- Mehtas of Rosy Blue Diamonds
- Bhawarlal Jain of Jain Irrigation Systems
- Sudhir and Samir Mehta of Torrent Group