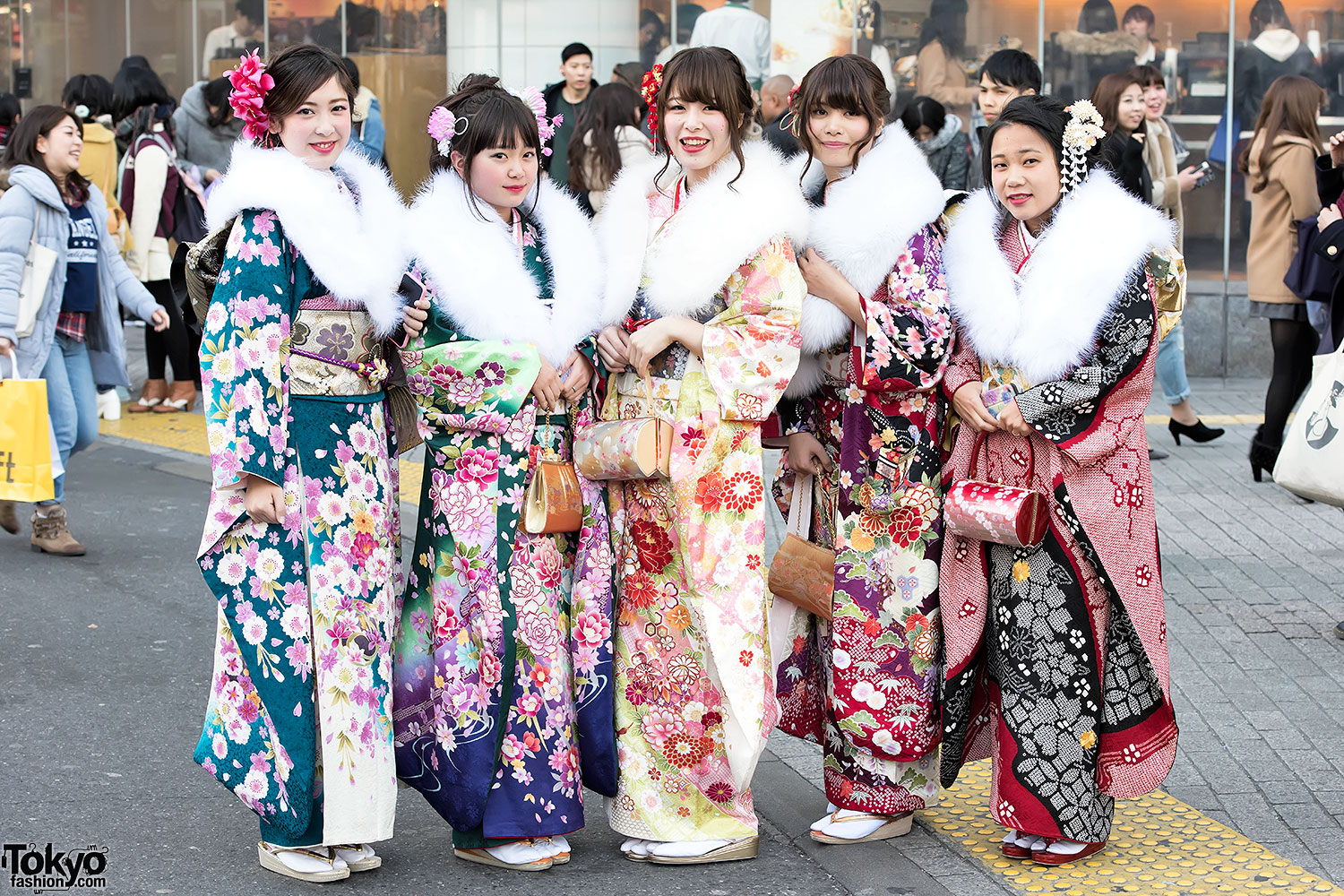
Vintage kimonos, often regarded as family heirlooms and passed down through generations, are piling up in Japan’s second-hand markets as the garments fall out of fashion and the country’s population shrinks. Traditionally the long, loose attire is wrapped around the body in a series of precise folds, lifts and adjustments in a dressing process that could take 25 minutes or longer. Now designers are repurposing high-quality fabric from cast-off kimonos to make contemporary outfits more suited to today’s sensibilities and fashion. The transformation is as much an art as science.
“People used to wear kimonos every day and now they don’t because it’s uncomfortable’’ says Duni Park, whose Tokyo-based Gallery Shili, transforms garments from Japan and her native South Korea into jumpsuits, shirts and scarves. “If things are to be continued to be used they must evolve with lifestyles.’’
Park, who has been selling her clothing online and in pop-up shops in department stores such as Takashimaya for the past few years, is part of a circular economy movement that aims to extend the life of products. It’s a trend that even some major retailers support as they use worn garment resales both to limit their climate impact and appeal to younger buyers.
Between 50% and 60% of the 140,000 metric tons of textiles gathered through collection services at H&M Group brands such as H&M, & Other Stories and Weekday have been directed to re-use and re-wear purposes. The Swedish fashion giant is also a majority shareholder in the second-hand online clothing retailer Sellpy. US outdoor clothing retailer Patagonia Inc. allows customers to buy or trade in used clothing and gear through its Worn Wear website and encourages repairs through its shops.
Fabric quality is a key factor in the ability to reuse or repurpose clothing and many of the garments that are produced in the “fast fashion kind of retail’’ have a much shorter life trajectory, according to Bryony Collins, an editor at BloombergNEF. Historically, kimonos were made from materials including silk, cotton or wool, although newer versions also come in synthetics.
Kimonos used to have a lifecycle that benefited entire families and communities and lasted decades or longer. After the garments were too worn out to be used as clothing, they could be used as cushion covers and then rags or baby diapers before finally being burned and spread over fields as fertilizer, according to Eisaku Hida, founder of Kimonoya Japan, an online marketplace. (Source: hindustantimes.com/Bloomberg)